Scientists may have just cracked the sun's greatest mystery (www.space.com)
Newly discovered fast magnetic waves might explain why the sun's corona is so hot.

This magazine is from a federated server and may be incomplete. Browse more on the original instance.
Newly discovered fast magnetic waves might explain why the sun's corona is so hot.

The James Webb Space Telescope has spotted water vapour in an area where planets may be forming, which could present an answer to the debate over how Earth got its water
This week, the European Space Agency will guide its dead Aeolus wind satellite back to Earth — but not in one piece.


New research conducted by scientists from NASA and Japan’s Osaka University suggests that rogue planets, or worlds that drift through space untethered to a star, significantly outnumber planets that orbit stars. The results indicate that NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope, scheduled for launch

"This result does not fit in with the currently accepted cosmological models, which include dark matter."

In a rare astronomical event, August 2023 stargazers will see two supermoons, coupled with the appearance of an elusive blue moon

NASA's unprecedented asteroid experiment is still churning out results.

As a new space race heats up, two researchers from the Kansas Geological Survey at the University of Kansas and their colleagues have proposed a new scientific subfield: planetary geoarchaeology, the study of how cultural and natural processes on Earth's moon, on Mars and across the solar system may be altering, preserving or...

The Solar System is a fairly tidy place.

Its believed Booster 9 and Starship 28 will be the next combination to fly

We have no explanations for this sort of slow repeat.

A Southwest Research Institute-led team has modeled the early impact history of Venus to explain how Earth's sister planet has maintained a youthful surface despite lacking plate tectonics. The team compared the early collision histories of the two bodies and determined that Venus likely experienced higher-speed, higher-energy...

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover sealed the tube containing its 20th rock core sample on June 23 (the 832nd Martian day, or sol, of the mission), and the mission's science team is excited about its potential. That's because this sample was drilled by the rover from an outcrop composed of tiny chunks of other rocks that were...

New research led by Newcastle University and published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society has revealed that supermassive black holes obscured by dust are more likely to grow and release tremendous amounts of energy when they are inside galaxies that are expected to collide with a neighboring galaxy.

VIPER is NASA’s first rover that needs headlights.


#space #rocketlab
The jug-like structure is a rare and short-lived double-lobed planetary nebula.

While U.S. Space Force thus far has split National Security Space Launch (NSSL) between SpaceX and United Launch Alliance (ULA), the service plans to have one more provider by the end of NSSL Phase 3 to guarantee Space Force can reach high-priority orbits when needed.

Studying the hydrogen fingerprint from just after the Big Bang could allow researchers to kill 'two birds with one stone!'

The 'ultracool' star is possibly around 44 times as dense as our solar system's largest member—the gas giant Jupiter.

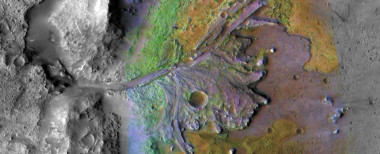
Materials found in the rocks of Mars' Jezero Crater suggest that organic matter may be widespread across the red planet.